What Exactly is Semantic Search?
In the simplest terms, semantic search is an SEO strategy used to improve search engine accuracy by understanding the “semantics” or meaning of what a user is searching for.
Rather than just ranking websites based on a few keyword matches, search engines are improving their search accuracy by trying to understand intent and contextual meaning behind the words users are inputting in their search bars. Basically, semantic search is way for Google and other search engines to provide better and more relevant results for their users.
How does semantic search work?
With semantic search, search engines take into account the following:
- User search history, as what users searched for in the past may help to indicate what they might want to see for future inquiries
- Location, which helps search engines provide relevant geographical results
- Query characteristics, which include spelling variations of specific words, including even misspelled words, or synonyms (where multiple words can have the same meaning)
- Logic and intent, which are understood using the help of word-sense disambiguation: “In computational linguistics, word-sense disambiguation (WSD) is an open problem of natural language processing and ontology. WSD is identifying which sense of a word (i.e. meaning) is used in a sentence, when the word has multiple meanings”
Let’s take a look at a few examples of how these factors work in every day search scenarios.
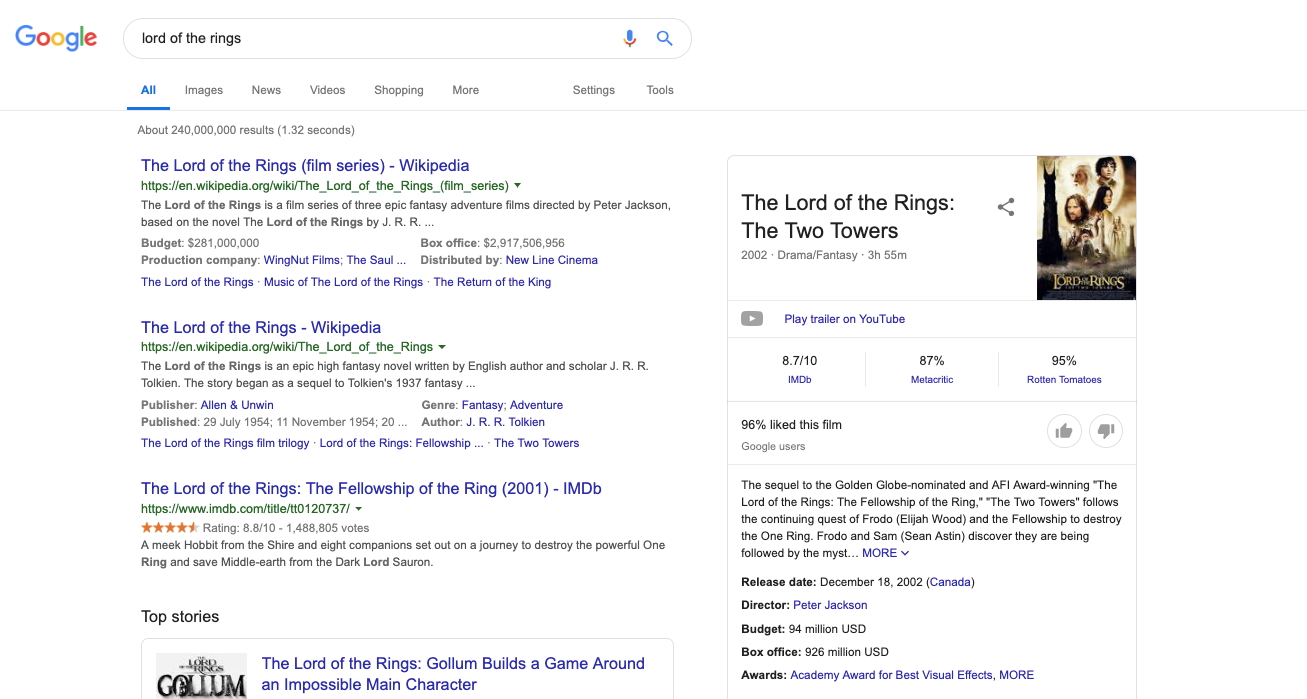
Knowledge Graph
Google has a massive interconnected network of data, known as the Knowledge Graph. This database is used to enhance search results by adding useful facts and information to the top of your results page. For example, search for “Lord of the Rings” and you’ll see additional information pop up on the right-hand side of the SERPs.
This Knowledge Graph data ensures users are provided with any additional useful information available that pertains to their original search.
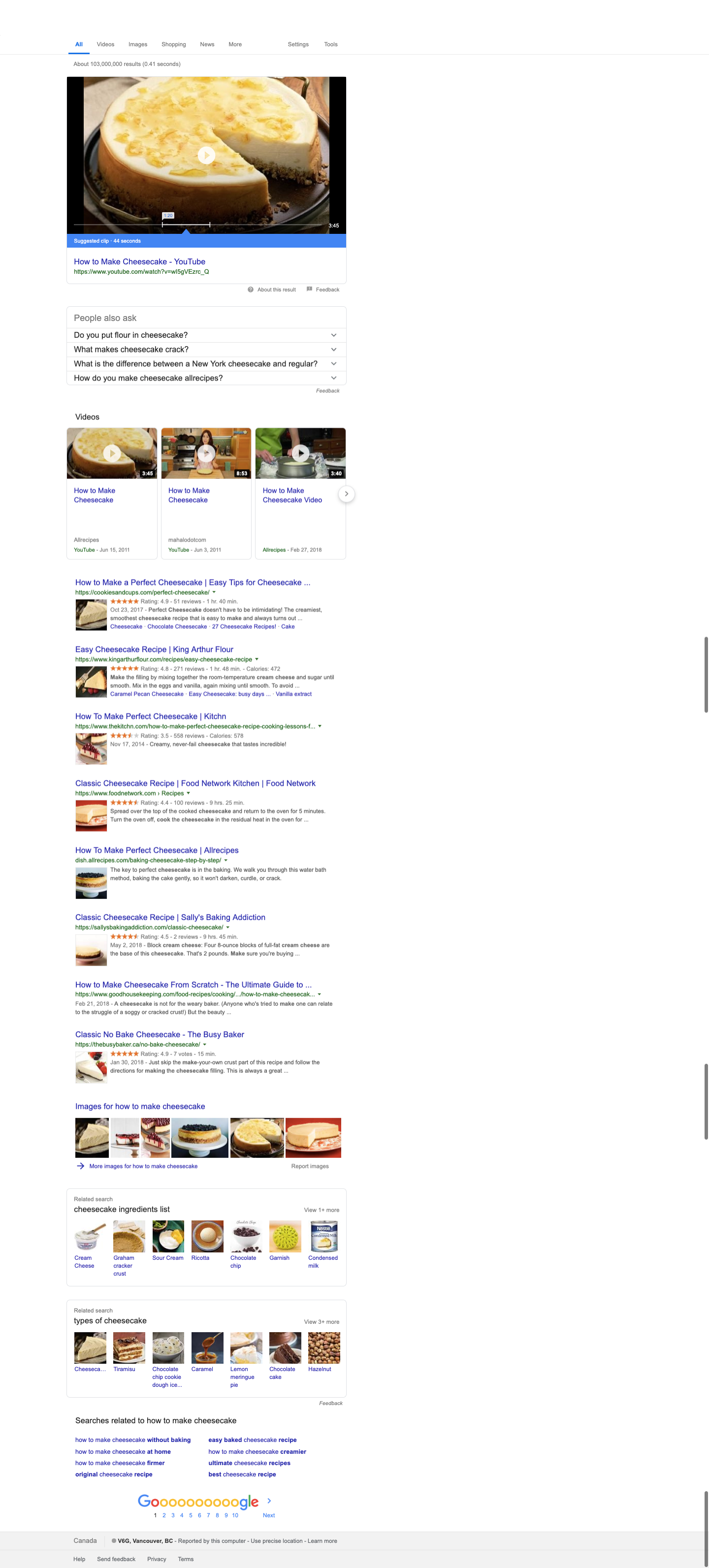
Conversational Queries
When searching for a long-tail keyword like “how to make cheesecake”, Google doesn’t just provide results for the phrase “how to make” — which would mean we’d never be able to find what we are looking for! Instead, Google understands the intent of the full question and will, again, present additional useful information to make your results as relevant as possible.
Take note of the suggested video, the “people also ask” similar queries, and the “related search” sections at the bottom, including a separate list of semantic search suggestions at the very bottom.
Voice Search
A recent Google Study has determined that 1 in 5 searches are being done through Google Voice Search. Siri, Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and other virtual assistants now allow users to search for what they want online using spoken word vs. typed. However, most people speak differently than they type, which means slang and even dialect need to be taken into account in semantic search results.
As detailed in our recent post on the implications of Big Data on marketing strategies, Big Data and machine learning are working together with search engine algorithms to constantly evolve and grow to incorporate natural language searching.
Now that you know what semantic search is…
You need to know how to incorporate it into your SEO strategy and your website. We go over this in detail in our post “How To Update Your Website for Semantic Search”. This post will help ensure you provide a better site search user experience and serve content to your visitors in a way that truly resonates. Check it out!